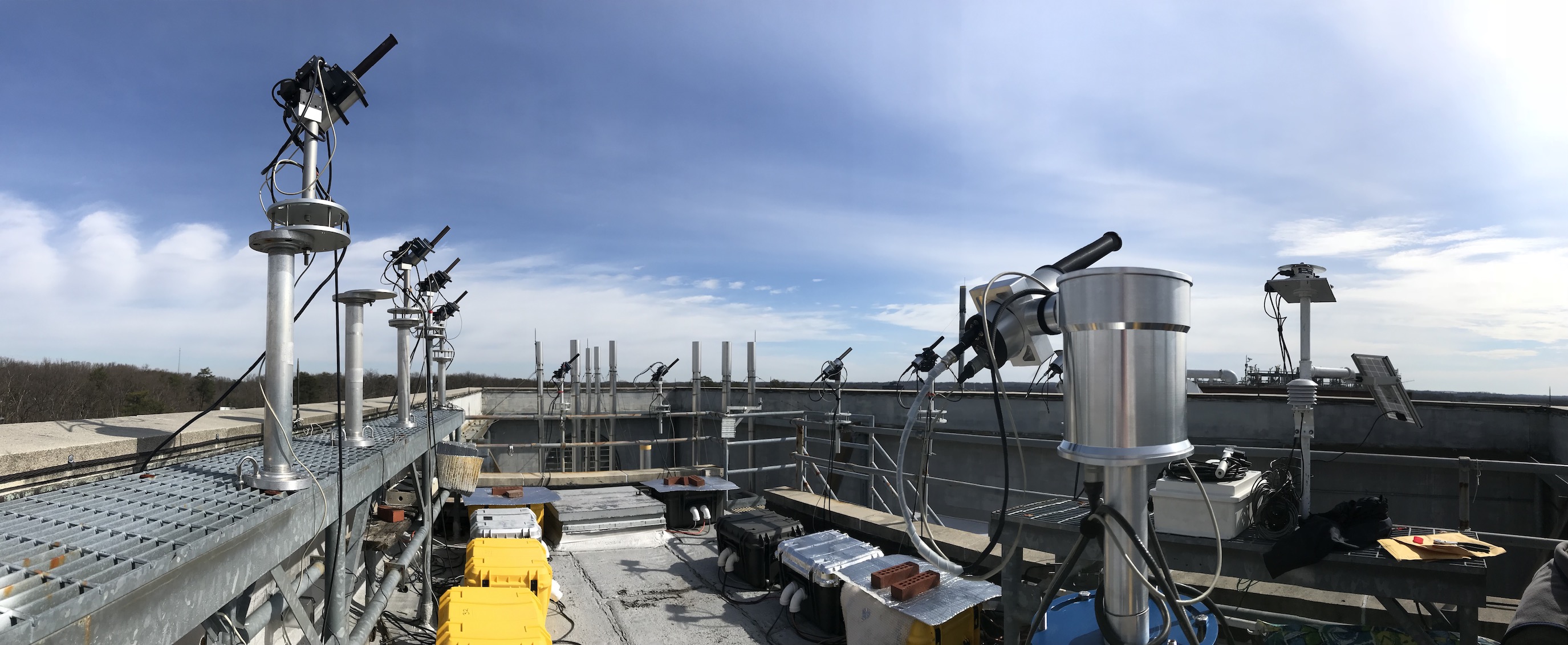
The Pandora Instrument
Pandora spectrometer instrument spectroscopy is used to measure columnar amounts of trace gases in the atmosphere. These gases (O3, NO2, CH2O)
absorb specific wavelengths of light from the sun in the ultraviolet-visible spectrum.
Using the theoretical solar spectrum as a reference,
Pandora determines trace gas amounts using differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS). This principle attributes differences in spectra measured by Pandora to the
presence of trace gases within the atmosphere (i.e. the difference between the theoretical solar spectrum and measured spectrum is
caused by absorption of trace gas species).
Using DOAS, Pandora is able to retrieve data with a temporal resolution of 80 seconds.
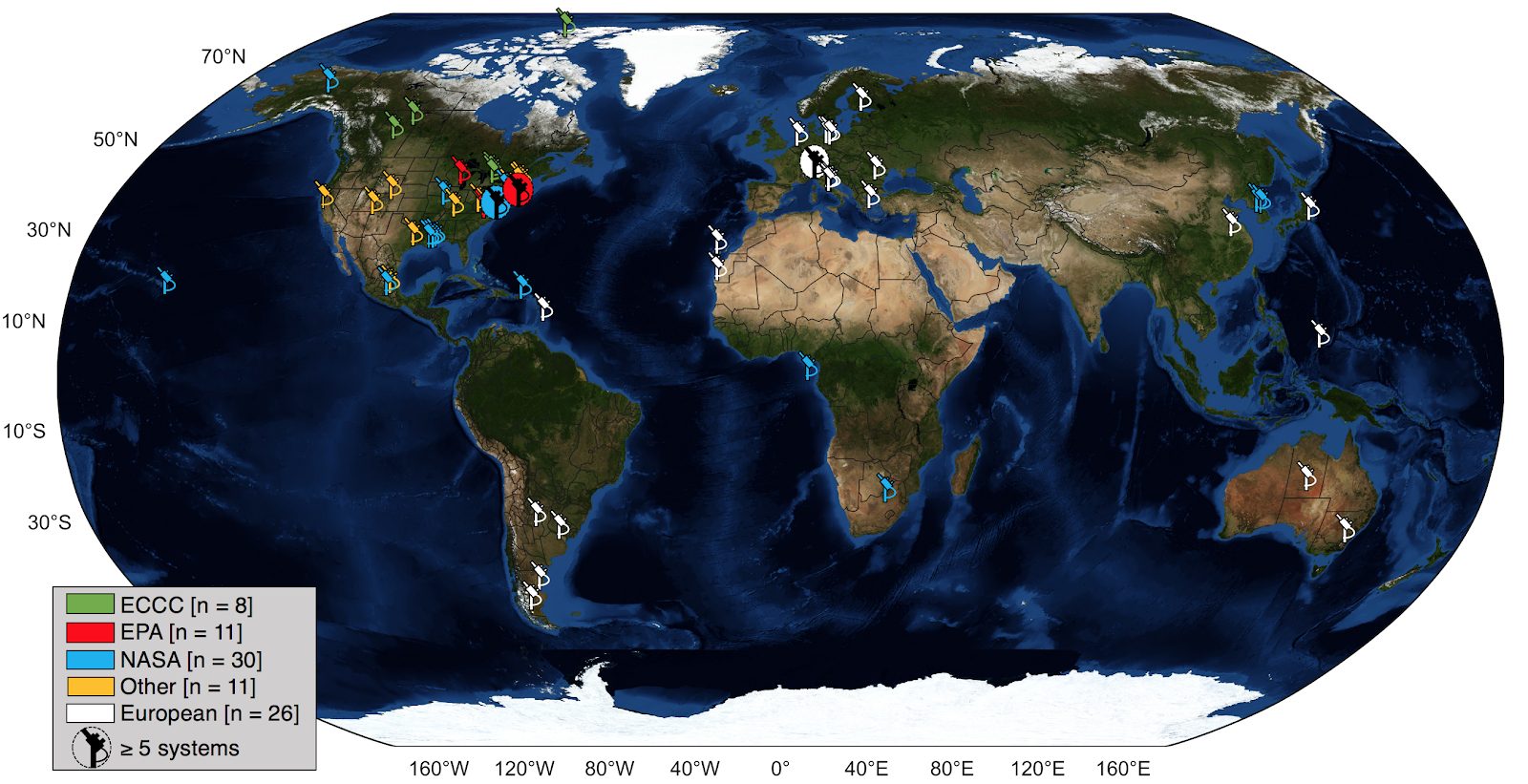
The Pandonia Global Network is used to monitor trace gas values worldwide. With a multitude of instruments collecting data daily,
the Pandora team is able to obtain information about the behaviors these gases have in the atmospheric column.
The raw data collected enters a vigorous filtering and processing cycle which produces the final data product with very high accuracy.
Used synonymously with other instruments, Pandora is able to validate collected data and extend the range of data collected
on gases in the atmosphere. Today, Pandora instruments are distributed at over 100 locations worldwide and is a continually growing project.